The Big Web3 E-Commerce Transformation
Published on Oct 29, 2024

The journey of e-commerce began in the early 90s, a time when the
internet was still in its infancy…

On August 11th, 1994, Dan Kohn, founder of NetMarket, sold a CD of Ten
Summoner’s Tales by Sting to a friend in Philadelphia. This sale is
recognized as one of the first encrypted online transactions using a
credit card, and although seemingly minor at the time, it marked the
beginning of what would become an important period in retail.
The 90s saw the rise of online marketplaces like Amazon and eBay, who
capitalized on the growing accessibility of the internet to create
completely new shopping experiences. Early on, e-commerce was in
essence, just basic websites offering limited functionality, and
transactions were rudimentary, often involving simple catalogs and
email forms, (Shudders), the focus was on providing convenience by
allowing customers to purchase items without leaving their homes.
The user experience however, was far from what we would expect today.
Early adopters had to navigate slow-loading websites, limited payment
options, and a big lack of trust in transacting online. This did begin
to shift though with the emergence of platforms like Amazon, who
started to redefine the possibilities of online shopping.
“E-Commerce is changing the way the world shops” — Jeff Bezos

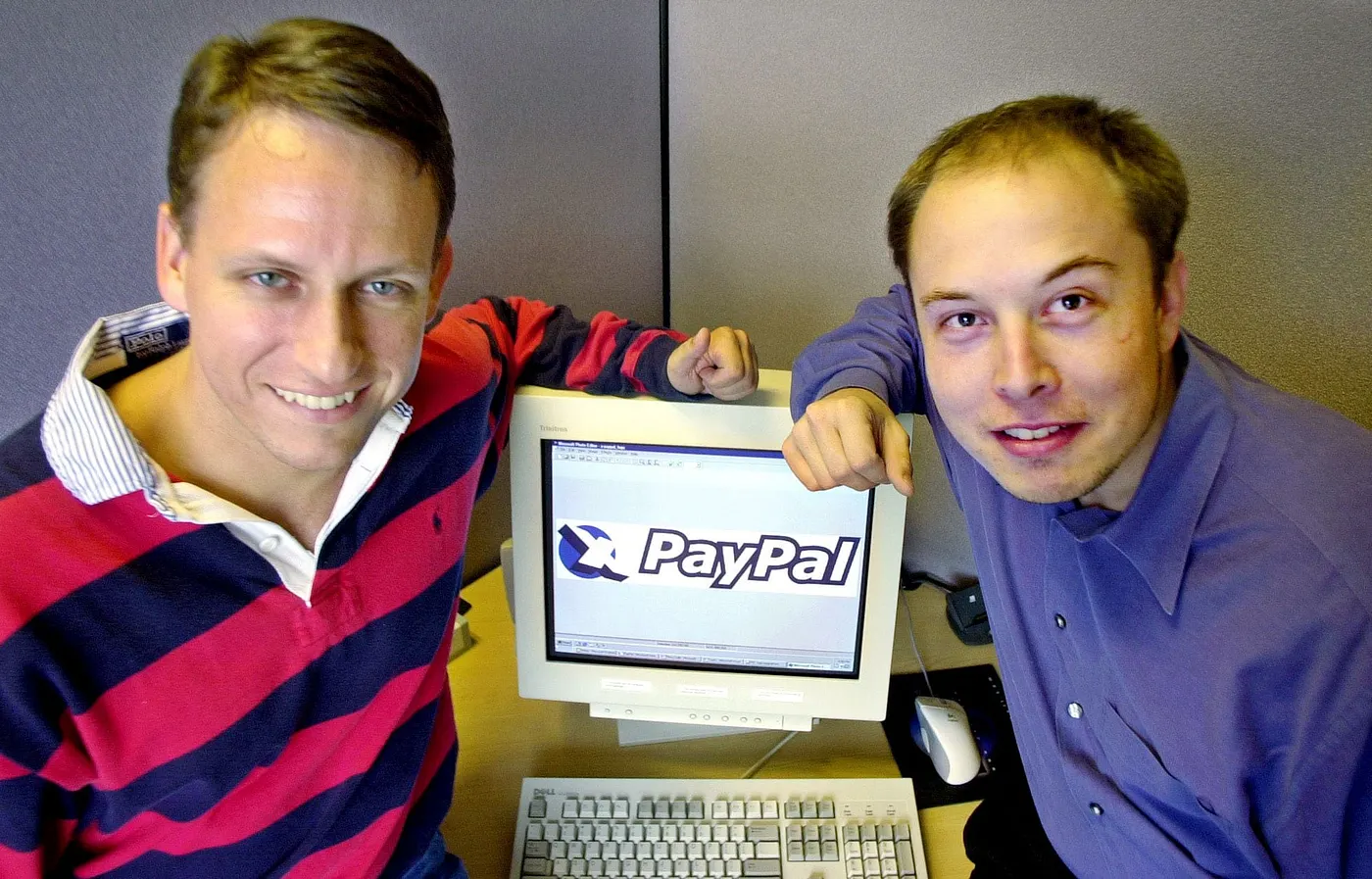
As we dived head-first into the 2000s, the Web2 boom began to reshape
e-commerce. Secure payment systems, such as PayPal were introduced,
which made online shopping far safer and much more convenient,
attracting a bigger audience.

Broadband internet, coupled with advancements in web design, also
allowed for much more dynamic and user-friendly online store fronts.
Social media platforms got in on the action too, integrating shopping
features that blurred the lines between browsing and buying.
The 2010s saw the rise of mobile commerce (m-commerce), as smartphones
became ubiquitous. This period witnessed the integration of social
media and e-commerce, with platforms like Instagram and Facebook
allowing users to shop directly from their public feeds. The
convenience of shopping from a mobile device completely embedded
e-commerce into the daily lives of consumers, making it a dominant
force in retail.

However, despite how far it’s come, traditional e-commerce struggles
with some clear limitations, and it has issues that are deeply rooted
in the very architecture of the Web2-based systems that continue to
dominate much of the industry’s infrastructure.

Data Privacy and Security

One of the biggest challenges in traditional e-commerce is the lack of
data privacy and security.
Centralized platforms accumulate disgustingly vast amounts of personal
information, making them a prime target for hacker groups. In 2017,
the Equifax incident exposed the personal data of 147 million people,
showcasing the extreme vulnerabilities present in centralized data
storage.
People are becoming more aware of these risks and want more control
over their data. However, the centralization of Web2 platforms makes
this difficult, and much of the friction in traditional e-commerce,
especially in social commerce, arises from concerns about how personal
data is collected, used, and shared.
High Fees

Traditional e-commerce has high transaction fees imposed by payment
processors.
Platforms like PayPal and major credit card companies take a
percentage of each transaction, which can massively cut into the
profit margins of small businesses. For example, PayPal charges up to
2.9% per transaction, a cost that, for example, adds up quickly for
businesses in developing countries with high sales volumes. These fees
can be quite prohibitive, especially for small businesses trying to
compete with the larger players who can afford to simply eat the
costs.
Centralized Monopolies

E-commerce is dominated by a select few large platforms, such as
Amazon and Alibaba, who exert an incredibly high level of control over
the market. These companies essentially set the rules of engagement,
and in turn, this centralization undercuts and smothers competition,
making it difficult for smaller players to gain a foothold.
The deep level of centralization within these platforms also means
that they can change policies or fees at will, leaving businesses and
consumers with very little options for legitimate recourse.
Trust

Trust is essential for successful e-commerce, but it is often lacking
in traditional models.
The inability to verify the authenticity of sellers and products is a
huge issue, leading to fraudulent behavior. In cross-border e-commerce
for example, customers may hesitate to purchase from international
websites due to concerns over product authenticity and return
policies, and the lack of strong identity verification systems further
exacerbates the problem, making it difficult for online retailers to
trust the authenticity of their customers.
Nowadays, Web2 social platforms struggle to generate trust,
particularly for smaller brands, and users often face uncertainty when
encountering lesser-known sellers. The lack of verifiable customer
reviews and secure payment methods really holds back the overall
shopping experience, and showcases more of the limitations present in
traditional e-commerce models.
Customer Loyalty

E-commerce today is incredibly competitive, and customer loyalty is
difficult to achieve.
With countless options available at the click of a button, retaining
customers requires effort and resources. Many e-commerce platforms
struggle to create effective loyalty programs that can genuinely
resonate with customers, resulting in low retention rates. Traditional
loyalty programs often fail to engage customers because they offer
little value beyond basic discounts, which can be easily matched or
exceeded by competitors.

Web3 completely flips the script on e-commerce, putting users back in
control of their transactions, data, and relationships.
Uptick’s modular architecture, built on the Cosmos-SDK with EVM
compatibility, gives businesses the flexibility to adapt their
e-commerce platforms as needs change. Decentralized marketplaces with
a wide range of different sales models like UptickNFT.com allow buyers
and sellers to connect directly, lowering transaction fees and putting
data ownership firmly back in the hands of the user. This model
addresses privacy concerns while reducing reliance on monopolistic
e-commerce giants, creating a more balanced environment.
Uptick’s support for EVM and WASM-based contracts also allows
businesses to scale efficiently, whether they are handling complex
logistics or running large-scale campaigns. Smart contracts are able
to automate chargebacks, refunds, and order disputes, completely
simplifying operations, and providing more flexibility.
With the integration of decentralized social graphs, Uptick allows
users to carry their profiles, preferences, and connections across
platforms. This strengthens customer engagement and builds loyalty,
giving users more control over their experience and helping businesses
offer a smoother, customer-centered ecosystem.
Here are a few other ways Web3 is further driving this transformation:
Tokenized Business Models and Product Combinations

A key element of Web3 e-commerce is the tokenization of physical goods
and services, often referred to as Real World Assets (RWAs)
This process transforms offline assets into digital ones, enabling
their connection to DeFi, and allowing businesses to explore new
models that generate revenue across both primary and secondary
markets. Uptick enables businesses to tokenize products individually
or bundle them to create new revenue streams, offering these assets as
standalone items for users to trade or use as collateral in DeFi.
The full potential of Web3 e-commerce really starts to shine when
tokenized products are bundled together.
These bundles can be tailored to meet specific customer needs or
unlock exclusive services, boosting engagement and ways to create
revenue. Businesses might tokenize a popular product and package it
with a related service, such as a subscription or warranty, and these
bundles can generate initial sales revenue while also opening up the
secondary markets, giving customers the ability to trade or resell the
bundles on UptickNFT.com or other decentralized marketplaces.
This benefits the customer and provides businesses with a sustainable
avenue for continued revenue beyond the initial sale. Essentially,
tokenized product combinations allow businesses to offer more
tailored, and responsive e-commerce experiences in both the physical
and digital worlds, so everybody wins.
Incentivized Loyalty

Uptick reshapes the notion of loyalty using NFTs and RWAs
Improving how brands engage with customers in e-commerce, these
programs offer rewards that carry transferable value across brand
ecosystems, moving beyond the limitations of traditional loyalty
points.
Retailers can issue digital assets tied to purchases, giving customers
access to exclusive discounts, early product releases, or tokenized
ownership of physical goods. Token-based access such as private
events, product previews, or VIP content can be made accessible based
on the assets customers hold.
This model builds stronger customer relationships and creates new
revenue streams, offering meaningful rewards with tangible value, and
encouraging ongoing engagement where Phygital assets coexist.
Tokenized Memberships and Access Control

Uptick provides the means to tokenize memberships and access control,
where customers hold digital tokens that provide access to exclusive
services or communities. These on-chain memberships offer verifiable
proof of access and ownership.
A company could issue tokens granting VIP access to events, premium
customer support, or members-only products. Tokenized memberships
encourage customer loyalty, as the tokens themselves can gain value
and be sold or traded peer-to-peer, creating a mutually dynamic
relationship between businesses and their customers.
Data Privacy and Security

Uptick DID and the Decentralized Data Service allow for the
verification of identity and management of data without the storing
sensitive information on centralized servers, lowering the risk of
fraud and breaches, and giving users direct control over their
personal information.
All transactions are recorded immutably on-chain, and ZK Proofs (ZKPs)
boost this by enabling verifiable yet private data validation. For
example, one of the recent Uptick ecosystem apps includes Vouch, a
verifiable credential and DID issuance platform, which streamlines
credential verification, and enables trust between customers and
businesses, an issue that even conventional e-commerce platforms often
struggle to address.
New Revenue Streams

Uptick supports a variety of revenue streams, making it possible for
businesses to offer subscription models and pay-per-use services.
Uptick’s omnichannel payment modules offer support for fiat,
cryptocurrencies, and CBDCs, making sure that businesses have the
flexibility to operate across multiple financial ecosystems with as
little friction as possible. High fees from traditional processors
make small transactions quite impractical, but on-chain options lower
these costs.
ERC-20 and ERC-4337 standards play an important role in enabling these
features with ERC-20 creating fungible tokens that can be used across
platforms, and ERC-4337 introducing account abstraction, which allows
for bundled transactions and automated payments. This simplifies
wallet management and gas fees, enabling practical micro-payments.
These capabilities can open up a lot of new revenue streams in content
creation, on-demand services, and pay-per-access models. Businesses
can now charge for individual articles or videos, giving consumers the
option to pay for only what they need without committing to larger
purchases or long-term subscriptions.
Decentralized Customer Relationship Management (DCRM)

Decentralized Customer Relationship Management (DCRM) on Uptick
provides businesses with transparent tools for managing customer
relationships.
Unlike traditional CRM platforms anchored to centralized databases,
Uptick DCRM stores and processes customer data in decentralized
environments, providing a much higher level of privacy and control.
Users gain more control over their personal data, increasing trust
between customers and businesses, and companies benefit from an array
of direct insights into customer behavior, reducing dependence on
third-party platforms. This decentralized framework gives businesses
far greater independence and strengthens customer privacy to a much
higher degree.
Modular Infrastructure
Uptick offers modular infrastructure built on the Cosmos-SDK, enabling
businesses to develop customizable and adaptable e-commerce platforms
that fit their specific needs. Uptick’s modular framework integrates
NFT and RWA capabilities, helping businesses reduce fees, explore new
business models, and overcome limited control associated with
traditional platforms.
With support for EVM and WASM smart contracts, Uptick also provides
automated workflows that cut operational costs by removing
intermediaries. Payments can be released upon delivery confirmation,
offering smoother transactions. Merchants also gain the flexibility to
create tokenized loyalty programs, streamlining engagement without
adding complexity.
This kind of modular architecture allows businesses to adapt to market
demands, scale efficiently, and develop sustainable models, all while
minimizing reliance on centralized systems. Essentially, this offers a
foundation to empower companies to explore Web3 with ease.
Layer 2

As Web3 commerce continues to evolve, scalable infrastructure becomes
important to support growing volume. Uptick’s architecture maintains
high performance and security under varying conditions, meeting the
demands of everything from micro-transactions to large-scale
operations.
Layer 2 scaling solutions boost efficiency in this way by batching
smaller transactions off-chain, reducing gas fees while maintaining
decentralization. This is especially valuable for retail and
subscription models, where frequent, low-cost transactions are
essential.
Uptick’s system can dynamically adjust to changing workloads,
guaranteeing consistent operation even during high-traffic periods.
This scalability prevents bottlenecks and maintains a stable user
experience, giving businesses confidence that they can scale with
market demands.
Fully Decentralized
From day one, Uptick has embraced the true nature of decentralization,
with an aim to shift control from centralized platforms to users.
Traditional e-commerce often restricts access and imposes high fees,
but Uptick’s model allows merchants and consumers to retain ownership
and manage their data, transactions, and assets.
Decentralization is embedded across the Uptick Ecosystem, from
transaction processing, to decision-making, to asset management. This
approach aligns the platform with the values of Web3, building
transparency and trust at each layer. With these decentralized
structures in place, Uptick provides businesses with a fairer, more
efficient way to engage with customers while eliminating reliance on
intermediaries.
Interoperability

Interoperability is essential for Web3 commerce, where blockchains
often operate independently. Uptick solves this fragmentation with its
Cross-Chain Bridge (UCB) and IBC Protocols, enabling businesses to
transfer digital assets across networks without friction.
This cross-chain connectivity lets merchants access multiple
blockchain ecosystems, managing transactions for NFTs, RWAs, and other
tokenized assets. Uptick’s infrastructure smoothly supports both
EVM-compatible and Cosmos-based networks, allowing platforms to
maintain full functionality across ecosystems.
These tools give businesses the flexibility to manage operations
across blockchains, unlocking access to new markets and reducing the
limitations of isolated systems.
Decentralized Identity

Uptick addresses the importance of privacy and security with its
W3C-compliant Decentralized Identity (DID) integration. With Uptick
DID, users manage their identities independently, reducing the risks
of unauthorized access.
Uptick infrastructure offers secure, user-focused authentication,
building trust between businesses and customers, and its decentralized
identity tools are currently available to the public via Vouch and
Upward, simplifying verification processes, and allowing users to
interact with platforms without the need to repeatedly share sensitive
data.
This decentralized identity system improves security and the overall
user experience, especially at a time where data breaches are ever so
common.
Uptick Web3 Business Models

Uptick’s infrastructure powers new Web3 business models by enabling
businesses to implement token-driven frameworks for customer
engagement and revenue generation.
Tokenized loyalty programs give businesses a way to issue rewards that
work across platforms, moving beyond the constraints of traditional
points systems. These loyalty tokens integrate with real-time data
analytics, helping businesses adjust incentives based on user
behavior.
Programmable NFTs within Uptick’s framework enable different
strategies, such as NFTs that evolve through user interaction to
unlock exclusive content or enhanced privileges. These dynamic tools
help businesses build sustained customer engagement. Uptick
infrastructure can also support advanced monetization options,
including staking, fractional ownership, and tokenized dividends.
Businesses can explore new income streams through premium services,
gated access, or dividends linked to secondary market performance,
enhancing user participation.
Uptick’s infrastructure provides the foundation for businesses to
deploy scalable, token-based frameworks, and through the UCB and IBC
protocols, businesses can manage digital and physical assets across
multiple chains, extending their reach while maintaining simplicity.
EVM and WASM smart contracts integrate directly into these models,
automating processes such as payments, memberships, and reward
distributions.
This embedded automation reduces friction, allowing businesses to
focus on growth and the specific Web3 models that work for them.
Comprehensive Digital Asset Support

With support for a wide range of digital assets beyond the JPEG,
Uptick bridges the gap between physical and digital assets, offering
businesses flexible ways to tokenize goods and services. RWAs like
property or luxury goods can be fractionalized, opening ownership up
to a much wider audience.
Uptick’s programmable NFT protocol allows businesses to integrate
token-based rewards, enhancing customer retention with meaningful
incentives. Staking and leasing models also enhance engagement,
encouraging users to stay active within the Web3 Ecosystem.
UCB and IBC are complimentary, making sure that tokenized assets
remain accessible across multiple networks, and businesses can manage
their operations with secure ownership tracking and decentralized
identity tools, giving users full control over their assets while
building trust across multiple platforms.
Decentralized Data

Uptick’s Decentralized Data Service tackles some of the privacy
challenges in traditional e-commerce, empowering businesses and users
with full control over their data. Product information, transaction
histories, and customer records are securely stored across
decentralized networks, creating transparent, tamper-proof records
that enhance user trust.
Uptick Oracle strengthens this framework by delivering real-time data
feeds, enabling businesses to efficiently manage inventory and pricing
with up-to-the-minute accuracy. Access to both real-time and
historical data allows merchants to optimize operations, and improve
customer insights.
With the ability to retain full control over their data without
relying on intermediaries, businesses gain a clear competitive
advantage. Uptick’s decentralized approach effectively transforms data
management into a strategic asset, enhancing sovereign customer
relationships across Web3.

The evolution of e-commerce from the early days in the 1990s to the
current Web3 transformation is a story of technological advancement
and philosophical change. Traditional e-commerce has brought
convenience and accessibility to millions, but it is definitely not
without its flaws. Data privacy concerns, high transaction fees, and
centralized control are just a few of the challenges that have plagued
the industry.
Web3 offers improvements to these problems by decentralizing the
internet, empowering users, and enhancing security and transparency.
Uptick is at the center of this transformation, providing the
infrastructure needed to support the next generation of Web3
e-commerce.
Modular, scalable, interoperable.
Going by these foundational principles, Uptick is enabling businesses
to explore new business models, enhance customer engagement, and
provide ways to build more secure and user-friendly Web3 e-commerce
platforms.
As we inevitably move further into the depths of Web3 at an alarming
pace, the innovations enabled by Uptick and similar protocols could
change how we interact with modern commerce, creating a fairer and
more transparent online marketplace environment for everyone involved.
The shift to Web3 is both a technological upgrade and a philosophical
rethinking of how digital economies can function, with a necessary
focus on decentralization and user empowerment.





























